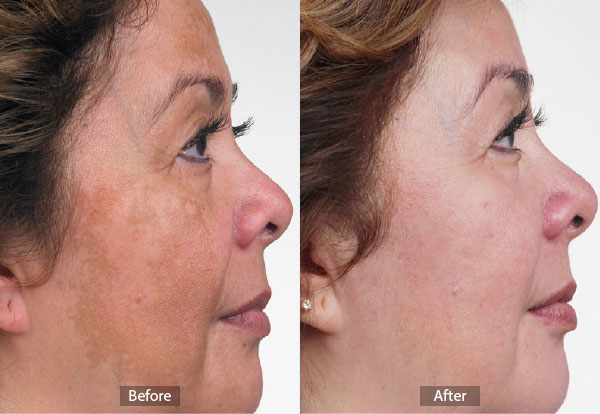
Hyperpigmentation is a common, usually harmless condition in which patches of skin become darker in color than the normal surrounding skin. This darkening occurs when an excess of melanin, the brown pigment that produces normal skin color, forms deposits in the skin.
Age or "liver" spots are a common form of hyperpigmentation. They occur due to sun damage, and are referred to by doctors as solar lentigines. These small, darkened patches are usually found on the hands and face or other areas frequently exposed to the sun.
Melasma or chloasma spots are similar in appearance to age spots but are larger areas of darkened skin that appear most often as a result of hormonal changes. Pregnancy, for example, can trigger overproduction of melanin that causes the "mask of pregnancy" on the face and darkened skin on the abdomen and other areas. Changes in skin color can result from outside causes. Other causes of dark spots are injuries to the skin, including some surgeries. Freckles are small brown spots that can appear anywhere on the body, but are most common on the face and arms. Freckles are an inherited characteristic. Freckles, age spots, and other darkened skin patches can become darker or more pronounced when skin is exposed to the sun. This happens because melanin absorbs the energy of the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays in order to protect he skin from overexposure.
Most prescription creams used to lighten the skin contain hydroquinone. Bleaches lighten and fade darkened skin patches by slowing the production of melanin so those dark spots gradually fade to match normal skin coloration. Prescription bleaches contain twice the amount of hydroquinone, the active ingredient, as over-the-counter skin bleaches. These are somewhat irritating to sensitive skin and will take 3-6 months to produce improvement.
There are now several highly effective laser treatments. The IPL Laser and other pigmented lesion lasers often remove pigment without scarring.